Why Choose a Gas Powered Hydraulic Pump for Your Heavy Lifting Needs
When it comes to heavy lifting needs, choosing the right equipment can make all the difference in productivity and efficiency. One option that stands out in the realm of hydraulic systems is the gas powered hydraulic pump. This versatile tool is designed to deliver reliable power and performance, making it an ideal choice for various industrial applications. Whether you are involved in construction, maintenance, or any task that requires lifting heavy loads, understanding the benefits of a gas powered hydraulic pump can help you make an informed decision.
Gas powered hydraulic pumps offer numerous advantages over their electric counterparts, most notably their portability and ability to operate in remote locations without the need for power outlets. This makes them invaluable for fieldwork and outdoor projects where electricity may not be readily available. Additionally, these pumps are typically more robust and capable of handling higher pressures, which translates into faster lifting times and improved efficiency in your operations. By exploring the functionalities and capabilities of gas powered hydraulic pumps, you can better appreciate why they are increasingly chosen by professionals facing demanding lifting challenges.
The Advantages of Gas Powered Hydraulic Pumps in Heavy Lifting Applications
When it comes to heavy lifting applications, gas-powered hydraulic pumps offer several distinct advantages that make them a preferred choice for many professionals in the industry. One of the primary benefits is their mobility. Unlike electric pumps, gas-powered hydraulic pumps are not tethered to a power source, providing operators with the freedom to work in remote locations or in areas without access to electricity. According to a report by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), nearly 60% of industrial lifting operations take place outdoors, where portable equipment is essential for efficiency and productivity.
Additionally, gas-powered pumps demonstrate superior power output and efficiency, particularly in high-demand scenarios. They can generate significant hydraulic force, often exceeding 5000 psi, making them ideal for lifting heavy machinery and construction materials. Data from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) indicates that gas-powered hydraulic systems can reduce lifting time by up to 30% compared to their electric counterparts, further enhancing productivity on job sites.
Another critical aspect is durability and ease of maintenance. Gas-powered hydraulic pumps typically feature robust designs that can withstand harsh conditions, which is crucial in rugged industrial environments. Industry analyses indicate that proper maintenance can extend the lifespan of these pumps beyond 10 years, making them a cost-effective investment for businesses that rely on heavy lifting. These factors combined position gas-powered hydraulic pumps as a strategic choice for those seeking reliability and performance in demanding lifting applications.
Advantages of Gas Powered Hydraulic Pumps for Heavy Lifting
This chart illustrates the key advantages of using gas powered hydraulic pumps in heavy lifting applications, showing the percentage benefits across various factors that influence lifting operations.
Key Factors Impacting Gas Powered Hydraulic Pump Performance Metrics
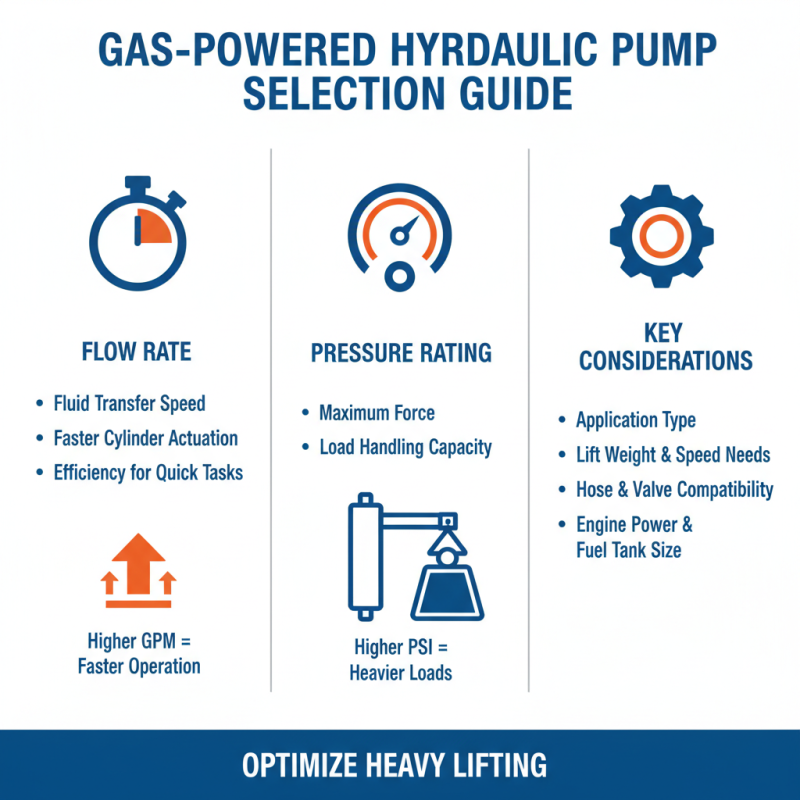
When selecting a gas powered hydraulic pump for heavy lifting applications, several key performance metrics come into play. An essential factor is the pump's flow rate, which determines how quickly it can transfer hydraulic fluid. A higher flow rate enables faster actuation of hydraulic cylinders, making it crucial for tasks requiring efficiency and speed. Additionally, the pressure rating is vital, as it signifies the maximum force the pump can exert, directly impacting the load it can handle.
Another critical aspect is durability and maintenance requirements. Gas powered hydraulic pumps are often subject to harsh working conditions, so selecting a unit made from high-quality materials will extend its lifespan and reduce downtime. Regular maintenance is also essential to ensure reliable performance; this includes checking oil levels, inspecting for leaks, and replacing filters as needed.
Tips: Always consider your specific lifting requirements when choosing a pump. Understand the weight limits and choose a pump that exceeds those specifications to ensure safety and reliability. Additionally, familiarize yourself with the pump's operating manual. Proper usage and maintenance can significantly enhance performance and longevity.
Comparison of Gas Powered and Electric Hydraulic Pumps for Heavy Lifting

When it comes to heavy lifting, the choice between gas-powered and electric hydraulic pumps can significantly influence performance and efficiency. Gas-powered hydraulic pumps offer unmatched portability and flexibility, making them ideal for outdoor applications or remote job sites where power sources may be limited. They typically provide higher pressure outputs, allowing for quicker lifting and more demanding tasks. Additionally, these pumps operate independently of an electrical grid, which can be a crucial advantage in industrial settings or during emergency situations.
On the other hand, electric hydraulic pumps bring a different set of benefits to the table. They are generally quieter and produce no harmful emissions, making them a more environmentally friendly option for indoor operations or settings where noise reduction is vital. Electric pumps also tend to have lower operational costs over time due to reduced fuel requirements and less maintenance. However, their reliance on electricity limits their use in areas without power supply, and they may not be able to achieve the same high pressure levels as their gas-powered counterparts in some cases. Ultimately, the choice depends on the specific lifting demands, working environment, and user preferences.
Industry Standards and Safety Regulations for Gas Powered Hydraulic Pumps
When selecting a gas powered hydraulic pump, it's essential to consider the industry standards and safety regulations that govern their use. These pumps are designed to handle high-pressure operations, which makes adherence to established safety protocols critical. Organizations like the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) provide guidelines that ensure operators understand the potential hazards and are prepared to mitigate risks. Compliance with these regulations not only protects personnel but also enhances the overall efficiency of operations.
Additionally, safety features are often integrated into gas powered hydraulic pumps to meet regulatory requirements. These features may include pressure relief valves, automatic shut-off systems, and protective casings. By prioritizing these safety elements, companies can reduce the likelihood of accidents and ensure that they are operating within the legal frameworks set forth by industry authorities. Regular training on the proper use and maintenance of these pumps, combined with adherence to safety regulations, can help create a safer working environment while maximizing the pumps' performance in heavy lifting tasks.
Why Choose a Gas Powered Hydraulic Pump for Your Heavy Lifting Needs - Industry Standards and Safety Regulations for Gas Powered Hydraulic Pumps
| Feature | Gas Powered Hydraulic Pump | Electric Powered Hydraulic Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Gasoline Engine | Electric Motor |
| Mobility | Highly Portable | Stationary/Requires Power Source |
| Typical Applications | Construction, Heavy Machinery | Automotive Repair, Light Operations |
| Weight | Generally Heavier | Generally Lighter |
| Safety Regulations | Must adhere to OSHA Guidelines | Must adhere to OSHA Guidelines |
| Noise Level | Higher Noise Output | Lower Noise Output |
Future Trends and Innovations in Gas Powered Hydraulic Pump Technology
As industries continue to embrace the capabilities of gas-powered hydraulic pumps, advancements in technology are shaping the future of heavy lifting. With the growing demand for efficient and reliable power sources, innovations such as variable speed motors and eco-friendly designs are being integrated into pump systems. According to a recent report by the Hydraulic Institute, the market for hydraulic pumps is expected to witness a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.4% through 2025, demonstrating the increasing reliance on sophisticated hydraulic systems across various sectors.
Moreover, the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) in hydraulic systems is revolutionizing how these pumps are monitored and managed. Real-time data analytics allows operators to track performance, optimize efficiency, and reduce downtime, thus enhancing productivity. The push for sustainability has also led to the development of hybrid models that combine gas-powered technology with electric systems, significantly minimizing carbon footprints while maintaining robust power output.
Tips: When considering a gas-powered hydraulic pump, evaluate the fuel efficiency and emission ratings to ensure compliance with environmental standards. Additionally, familiarize yourself with the latest technological advancements to leverage features that can streamline operations and improve operational efficiency in your heavy lifting tasks. Embracing these trends can significantly impact your project outcomes and contribute to sustainable practices within your industry.
Related Posts
-

How to Optimize Air Hydraulic Pump Performance for Maximum Efficiency
-

How to Optimize the Performance of Your Hydraulic Pump Motor
-

Unveiling Trends in Electric Hydraulic Pump Demand at China's 138th Canton Fair 2025: Market Insights and Growth Forecasts
-

The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Hydraulic Pumps and Motors for Efficient Machinery Performance
-

The Ultimate Guide to the Best 5 Air Hydraulic Pumps for Efficient Performance in 2023
-

2025 Top 5 Hydraulic Pumps and Motors You Need for Optimal Performance
Choose a global leader for your hydraulics solutions
How can we help you?
Call to 0034 943884600 Contact us
