What is a Hydraulic Motor and How Does it Work in Different Applications
Hydraulic motors are a pivotal technology in the realm of fluid power, converting hydraulic energy into mechanical energy to produce rotational motion. According to recent industry reports, the global hydraulic motor market is projected to grow at a significant rate, driven by increased demand in diverse sectors such as construction, agriculture, and manufacturing. With advancements in hydraulic engineering and technology, hydraulic motors are now capable of delivering high torque and efficiency, even in the most demanding applications.
The versatile applications of hydraulic motors span a wide range of industries, from powering heavy construction equipment to aiding in the precise movements of industrial machinery. Reports from the Hydraulic Institute indicate that the integration of hydraulic motors in automated systems has notably improved productivity and operational efficiency. As businesses seek sustainable and cost-effective solutions in an increasingly competitive environment, the role of hydraulic motors will continue to expand. Understanding how these motors work and their advantages over other types of motors can provide valuable insights for engineers and decision-makers aiming to optimize their operations.
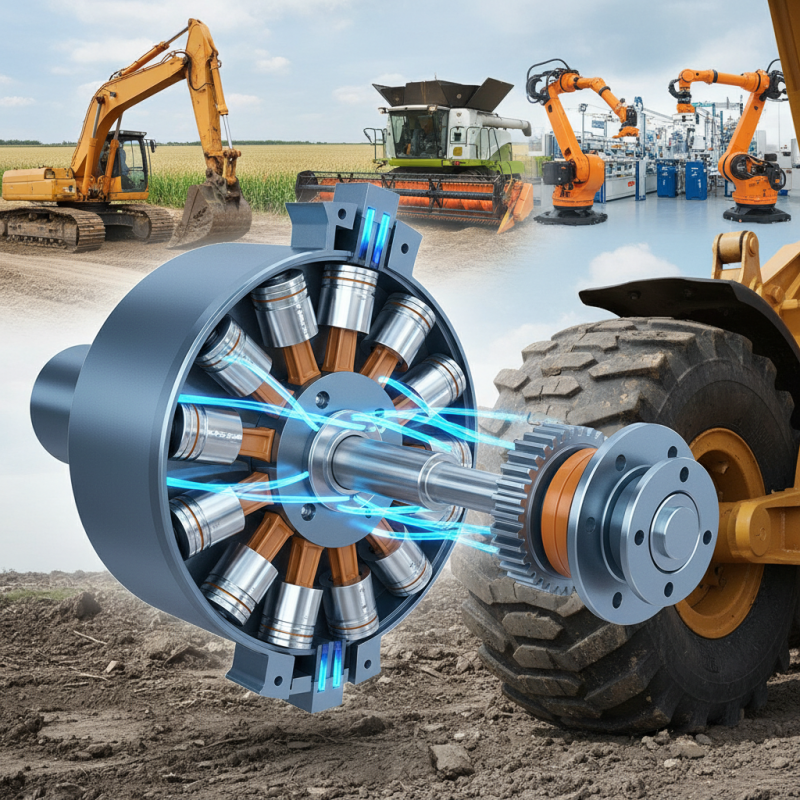

What is a Hydraulic Motor and Its Basic Components

Hydraulic motors are essential components in various industrial applications, converting hydraulic energy into mechanical work. They generally consist of several basic components: a housing or casing, an input shaft, a rotor, and a means of generating fluid pressure. Depending on their design, these motors can utilize different mechanisms, such as gear or vane designs, to create rotational motion. According to the "Hydraulic Equipment Market Trends" report published by Research and Markets in 2023, the hydraulic motor segment has been projected to experience a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% through 2025, reflecting their critical role in sectors such as construction, agriculture, and manufacturing.
One of the defining features of hydraulic motors is their efficiency in power-to-weight ratio. They provide high torque at low speeds, making them ideal for applications requiring significant force without large machinery overhead. For instance, in construction equipment like excavators, hydraulic motors enable precise control of movement and positioning, essential for optimizing operation in dynamic work environments. The global hydraulic motors market was valued at approximately $2 billion in 2022, as noted in the same report, underscoring their importance across multiple sectors where they facilitate complex operations with minimal energy consumption, highlighting their competitiveness against traditional mechanical motors.
The Operating Principles of Hydraulic Motors Explained
Hydraulic motors are pivotal components in various industrial applications, converting hydraulic energy into mechanical energy through a series of controlled actions. The operating principle of hydraulic motors relies on Pascal's Law, which states that a change in pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished throughout the fluid. When pressurized hydraulic fluid is directed into the motor, it acts on the motor's rotor, causing it to rotate. This rotational motion is then harnessed to perform work, such as driving machinery or vehicles. According to the Fluid Power Society, hydraulic motors are capable of delivering torque values ranging from as low as 0.3 Nm to over 5000 Nm, depending on their design and application.
In practice, hydraulic motors come in several types, including gear, piston, and vane motors, each suited for specific uses. For example, hydraulic gear motors are widely utilized in construction equipment due to their reliability and compact size, while hydraulic piston motors are favored in applications requiring high torque and efficiency, such as in mining machinery. A report by the International Hydraulic Committee states that the demand for hydraulic motors is projected to grow by 4.3% annually, driven by the expansion of mobile machinery and automation in manufacturing processes. This growth underscores the evolving role of hydraulic motors in enhancing productivity and energy efficiency across various sectors, making them a critical element in modern hydraulic systems.
Types of Hydraulic Motors and Their Specific Uses
Hydraulic motors are crucial components in various fields, functioning by converting hydraulic energy into mechanical energy. There are several types of hydraulic motors, each with specific applications that suit their design and operating principles. Gear motors, for instance, are compact and offer high torque at low speeds, making them ideal for applications like conveyor systems and winches. Their straightforward design allows for easy maintenance, which is a significant advantage in industrial settings.
Another common type is the vane motor, which utilizes sliding vanes to create motion. These motors provide a smooth operation and are typically used in applications requiring moderate speed and torque, such as agricultural machinery and material handling equipment. Their efficiency and ability to handle fluctuating loads make them a popular choice.
Lastly, piston motors are characterized by their high efficiency and power density. They are versatile and can be found in mobile equipment, such as excavators and loaders, where variable speed and high power output are essential. The ability to provide consistent torque across a wide range of speeds makes piston motors suitable for demanding applications in construction and manufacturing sectors. Each type of hydraulic motor, with its unique properties, is tailored to meet the specific demands of various industries, ensuring optimal performance in diverse environments.
Applications of Hydraulic Motors in Various Industries
Hydraulic motors are essential components in a variety of industries, providing reliable mechanical power to operate equipment. In construction, hydraulic motors are commonly used in excavators and bulldozers, where they convert hydraulic energy into rotational energy. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global hydraulic motors market is expected to reach $5.5 billion by 2025, driven largely by advancements in machinery and emerging applications in sectors like agriculture and manufacturing.
In the agriculture sector, hydraulic motors are prominently used in tractors and harvesting machines, enabling efficient operation of attachments such as plows and seeders. The versatility of these motors allows for smooth operation even under heavy loads, ensuring productivity and reducing downtime. Furthermore, in manufacturing, hydraulic motors play a crucial role in automation processes, powering conveyors and lifts. Monitoring and optimizing the hydraulic systems can yield significant improvements in efficiency, as traditional systems often experience energy losses which can be mitigated with newer technologies.
Tips: Regular maintenance of hydraulic motors is vital to extending their life and maintaining optimal performance. Check for fluid leaks and ensure that hydraulic fluid levels are adequate. Implementing monitoring systems can also provide insights into the efficiency and health of the motors, prompting preemptive maintenance before significant failures occur.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Hydraulic Motors
Hydraulic motors are widely used in various applications, ranging from construction equipment to automotive systems, due to their ability to convert hydraulic energy into mechanical torque. However, when considering the adoption of hydraulic motors, it is essential to weigh their advantages against their disadvantages. One of the notable advantages is their high power-to-size ratio. According to a report by the International Fluid Power Society, hydraulic motors can deliver up to 150% more torque than an equivalent electric motor at lower speeds, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications such as excavators and lift systems.
On the downside, hydraulic motors do have certain limitations. A significant disadvantage is their reliance on hydraulic fluid, which can lead to potential leakage issues that not only affect performance but also introduce environmental concerns. Additionally, hydraulic systems generally require more maintenance than electric or pneumatic systems. A study by the National Fluid Power Association highlights that around 20% of hydraulic systems fail due to poor maintenance practices. This indicates that while hydraulic motors are potent and efficient, users must approach their implementation with a comprehensive maintenance strategy to mitigate risks associated with leaks and system failures.
Related Posts
-

7 Best Hydraulic Motors for Efficient Energy Solutions in 2024
-

How to Choose the Right Hydraulic Pumps and Motors for Your Industrial Needs
-

5 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Hydraulic Pump Motor for Your Industrial Needs
-

How to Optimize the Performance of Your Hydraulic Pump Motor
-
Exploring Hydraulic Pumps and Motors Innovations at the 138th Canton Fair 2025: Industry Insights
-

The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Hydraulic Pumps and Motors for Efficient Machinery Performance
Choose a global leader for your hydraulics solutions
How can we help you?
Call to 0034 943884600 Contact us
