How to Understand Fluid Power Systems and Their Applications?
Fluid power systems are essential in many modern applications. They utilize pressurized liquids or gases to generate, control, and transmit power. The technology is widely used in industries like manufacturing, construction, and transportation. Understanding fluid power is crucial for engineers and technicians alike.
These systems can be complex. Many components work together, such as pumps, valves, and actuators. Each part must function correctly to ensure the system operates efficiently. There's also a need for careful design and maintenance. Small mistakes can lead to significant issues. Learning about fluid power involves practical experience and theoretical knowledge.
In daily applications, fluid power systems can be found in machinery, vehicles, and even robotics. Observing these systems in action provides valuable insights. However, misconceptions often arise regarding their reliability and efficiency. It's vital to keep questioning assumptions and improve our understanding of fluid power. Only then can we fully harness their potential.

Overview of Fluid Power Systems: Definition and Components
Fluid power systems play a vital role in various industries. They use liquids or gases to transmit power. Understanding these systems requires knowledge of their key components. Hydraulic fluids, pumps, motors, and actuators are essential parts of this technology. Each component contributes to the overall efficiency and functionality of the system.
Tips for maintaining fluid power systems include regular inspections. Check for leaks, wear, and signs of corrosion. Keeping the fluid clean is crucial to prevent contamination. Also, ensure that all seals and hoses are in good condition. Neglecting maintenance can lead to costly failures.
Moreover, it is important to understand how components interact. For instance, the wrong type of fluid can affect system performance. System design should consider factors like pressure and flow rate. A poorly designed system can waste energy and reduce effectiveness. Always assess the specific application to avoid these common pitfalls.
Overview of Fluid Power Systems: Definition and Components
| Component | Definition | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Pump | A device used to convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. | Used in excavators, forklifts, and other construction machinery. |
| Actuator | A component that converts fluid power into mechanical motion. | Applied in robotic arms and automated industrial equipment. |
| Accumulator | A storage device that holds hydraulic fluid under pressure. | Used to maintain pressure in hydraulic circuits and provide flow during peak demands. |
| Control Valve | A valve that regulates the flow and direction of hydraulic fluid. | Utilized in various applications for precise movement control. |
| Filter | A device that removes contaminants from hydraulic fluid. | Essential in maintaining system performance and longevity. |
Principles of Fluid Dynamics in Power Transmission
Fluid dynamics plays a crucial role in power transmission systems. By moving fluids, these systems efficiently transfer energy. According to the International Fluid Power Society, over 70% of industrial machinery uses fluid power in some capacity. This reliance showcases the importance of understanding fluid mechanics principles.
The key principles include Bernoulli's equation and Pascal's law. Bernoulli's equation describes how fluid speed affects pressure. Higher velocity means lower pressure. This principle is fundamental in hydraulic systems. Pascal's law states that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted equally in all directions. This principle is evident in hydraulic presses and lifts.
However, fluid power systems face challenges. Leakage can occur, leading to energy loss. A report by the National Fluid Power Association noted that inefficient systems can lead to up to 15% energy waste. Understanding the dynamics of fluid movement can help address these inefficiencies. It requires continuous evaluation and innovation to improve system design and reduce waste.
Applications of Fluid Power in Industrial and Mobile Systems
Fluid power systems play a crucial role in various industrial and mobile applications. In manufacturing, hydraulic systems are widely used. According to a report by the International Fluid Power Society, hydraulics can increase efficiency by up to 30%. This is significant. However, many companies still face challenges in optimizing these systems.
In mobile applications, fluid power is essential for equipment like construction machinery and agricultural vehicles. The demand for these applications is rising. A recent study highlights that the global hydraulic market is expected to reach $47 billion by 2027. This growth reflects the increasing reliance on fluid power. Yet, operational issues frequently arise.
Leakages and maintenance can lead to inefficiencies. Many operators overlook regular checks, risking performance drops. It’s vital to adopt a proactive approach to maintenance. By monitoring fluid levels and system integrity, companies can enhance their operational capabilities. Addressing these issues ensures that fluid power systems function effectively and sustainably across diverse applications.
Applications of Fluid Power in Industrial and Mobile Systems
This chart illustrates the percentage application of fluid power across various industries, showcasing its significant role in sectors such as manufacturing, construction, agriculture, automotive, and marine.
Advantages and Limitations of Fluid Power Technology
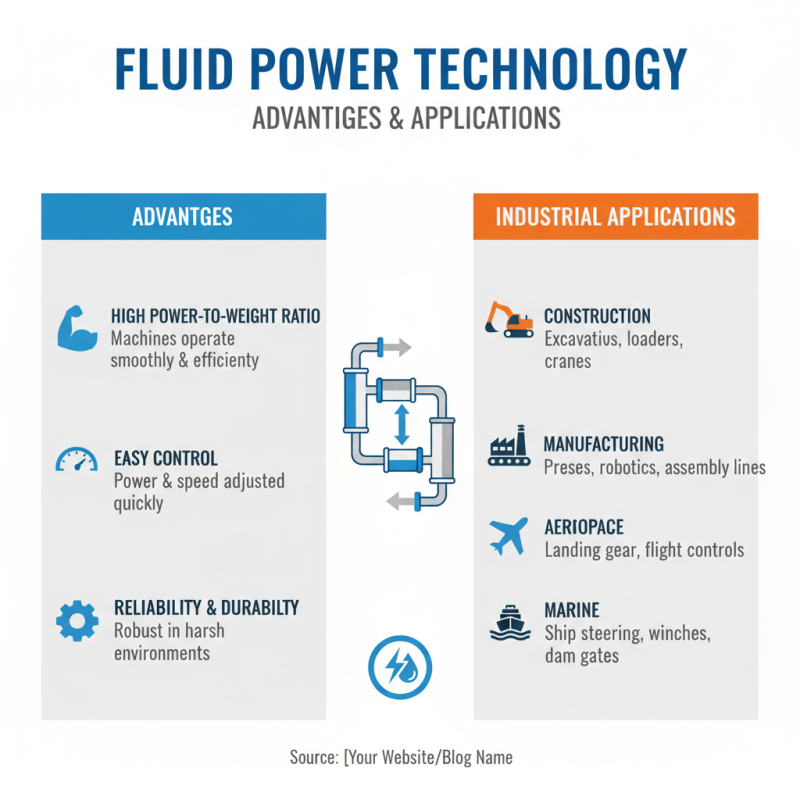
Fluid power technology is widely used in various industries. It offers many advantages. For instance, it provides high power-to-weight ratios. This allows machines to operate smoothly and efficiently. Fluid power systems are also easy to control. They can adjust power and speed quickly.
However, there are limitations to consider. Fluid leakage can lead to maintenance issues. It may also result in environmental concerns. The systems can be complex and require skilled operators. Furthermore, initial setup costs can be high. Some may find these drawbacks challenging to manage.
Ultimately, understanding both advantages and limitations is essential. This helps in selecting the right fluid power system for specific applications. Engineers must weigh efficiency against potential downsides. In this way, fluid power technology can be leveraged effectively.
Future Trends in Fluid Power Systems and Innovations
As industries evolve, fluid power systems are also adapting to new demands. The future holds exciting innovations. For instance, the integration of IoT technology is transforming how we monitor these systems. Smart sensors provide real-time data on performance. This helps anticipate failures, enhancing efficiency and safety.
Another trend is the shift toward more sustainable practices. Engineers are exploring bio-based hydraulic fluids. These alternatives are less harmful to the environment. Companies are also investing in energy-efficient designs. This not only reduces waste but also cuts operational costs.
However, challenges remain. The transition to new technologies can be slow. Some businesses hesitate to invest in unproven systems. As a result, there's a risk of falling behind competitors. It’s crucial to balance innovation with practical implementation. Adapting quickly is not always easy, but it is necessary for future success.
Related Posts
-

Unlocking the Secrets of Fluid Power Mechanics for Everyday Applications
-

Unveiling the Future of Fluid Power Hydraulics in Sustainable Engineering
-

Top 10 Hydraulic Equipment You Need for Your Business Success
-

7 Compelling Reasons to Choose Fluid Power Hydraulics for Your Industrial Needs
-

Innovative Solutions for Fluid Power Hydraulics Efficiency
-

How to Optimize Your Operations with Innovative Hydraulic Solutions
Choose a global leader for your hydraulics solutions
How can we help you?
Call to 0034 943884600 Contact us
